Procedures
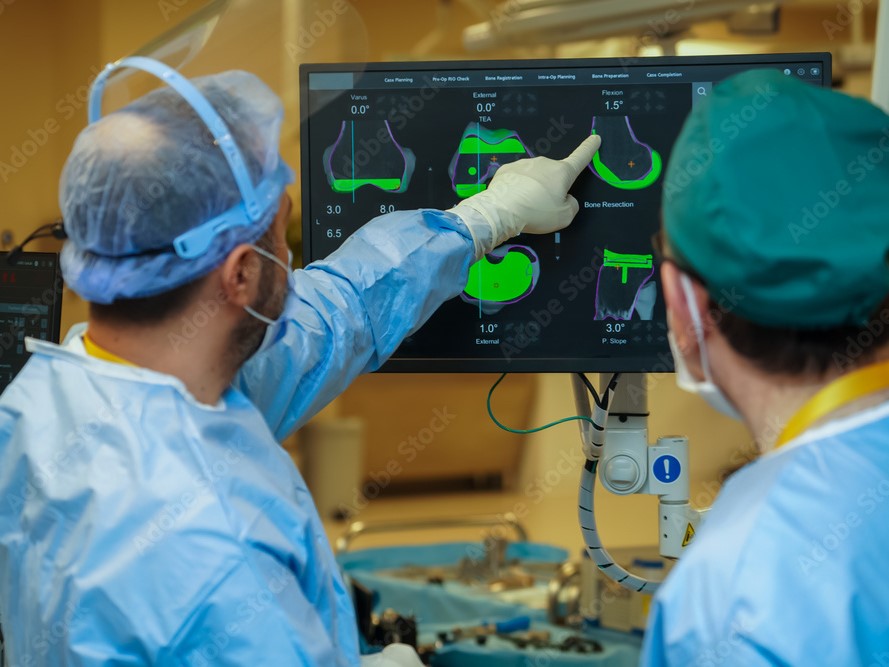

Robotic total knee replacement (TKR) is an advanced surgical procedure utilizing robotic systems to enhance precision in knee joint replacement. These systems assist us by providing 3D preoperative planning and real-time intraoperative guidance, ensuring accurate alignment and positioning of implants.
This precision reduces errors, improves implant longevity, and enhances patient outcomes. Benefits include shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and improved joint function. This technology represents a significant advancement in orthopedic surgery, offering personalized and highly effective treatment options.
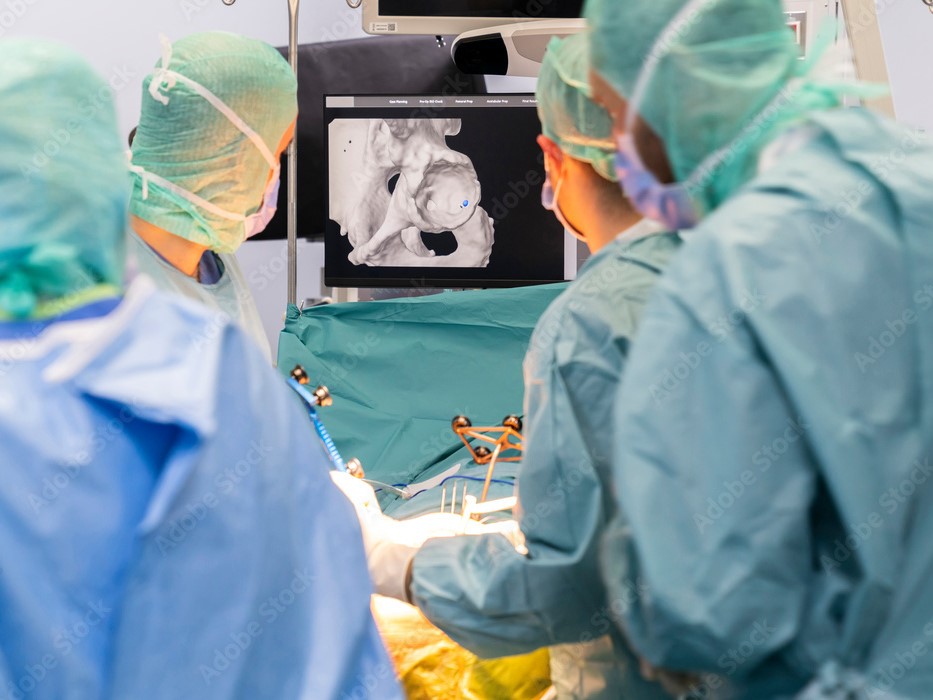
Robotic total hip replacement is an advanced surgical procedure utilizing robotic technology to enhance precision and outcomes. We use robotic systems to create a 3D model of the patient’s hip, allowing for detailed preoperative planning. During surgery, the robot assists in the accurate placement of implants, reducing the risk of human error and improving alignment.
This technology results in less tissue damage, quicker recovery times, and potentially longer-lasting implants. Patients often experience reduced pain and better mobility post-surgery. Robotic assistance in hip replacement exemplifies the integration of technology to improve the efficacy and safety of orthopedic surgeries.
Indications and Evaluation:
- Patient Assessment: Candidates are evaluated based on pain, limited mobility, and joint damage affecting daily life.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays and sometimes MRI or CT scans assess the severity of joint damage.
Preoperative Preparation:
- Medical Evaluation: Checking overall health and addressing any existing conditions before surgery.
- Educational Sessions: Patients receive information about the procedure, recovery, and postoperative care.
Anesthesia and Incision:
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered based on the patient’s health and preferences.
- Incision: Surgeons make an incision, typically on the front of the knee, to access the joint.
Reshaping and Preparation:
- Bone Reshaping: Damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the femur, tibia, and kneecap.
- Implant Placement: Metal and plastic components replace the removed surfaces, reconstructing the joint.
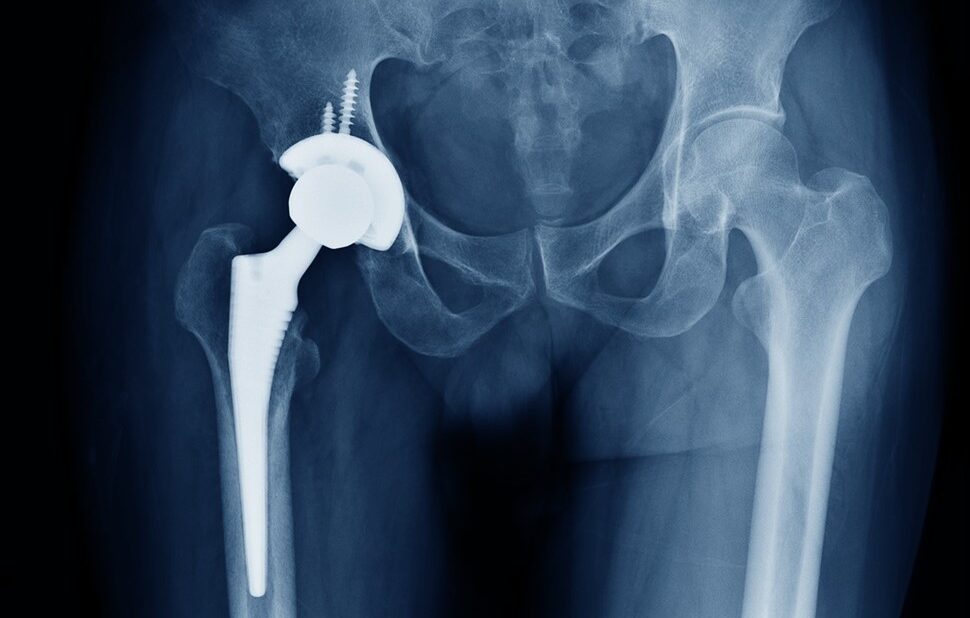
Preoperative Assessment:
- Patient Evaluation: Assessment of pain, limited mobility, and impact on daily activities due to hip joint issues.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are used to evaluate the extent of joint damage.
Preparation and Planning:
- Medical Evaluation: Ensuring the patient’s overall health and addressing any existing conditions before surgery.
- Patient Education: Providing information about the procedure, expected outcomes, and postoperative rehabilitation.
Anesthesia and Incision:
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered based on patient and surgeon preferences.
- Surgical Access: Surgeons make an incision, often on the side or back of the hip, to access the joint.
Hip Joint Reshaping:
- Bone Preparation: Damaged bone and cartilage are removed from the hip socket (acetabulum) and femur.
- Implant Placement: Metal or ceramic implants replace the damaged joint surfaces, reconstructing the hip joint.

Revision total knee replacement is a surgical procedure to replace or repair a problematic knee prosthesis from a previous knee replacement. This surgery addresses issues such as implant loosening, infection, instability, wear, or damage. .
The procedure involves removing the old implant, preparing the bone surfaces, and fitting new prosthetic components. Recovery can be longer and often requires extensive physical therapy to restore function and mobility. Success rates vary, but many patients experience significant pain relief and improved joint function.
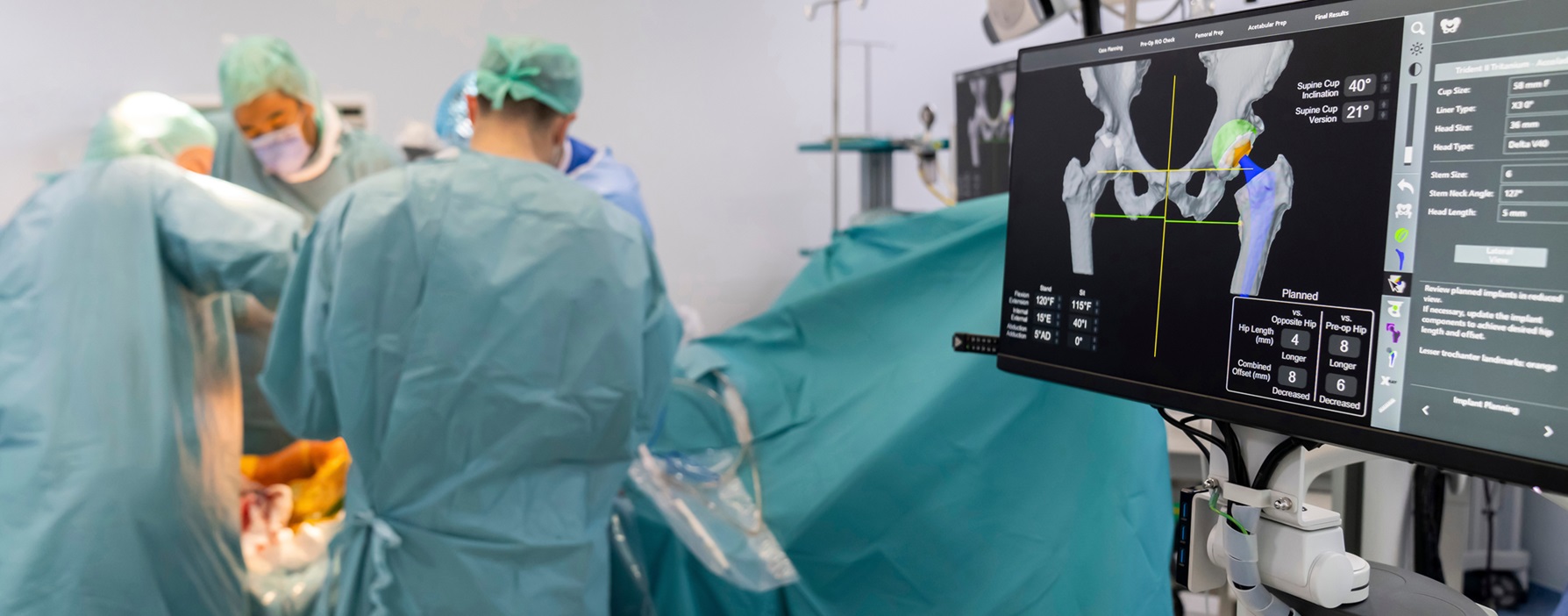
Revision total hip replacement is a surgical procedure performed to replace a previously implanted artificial hip joint that has failed. This failure can result from wear and tear, infection, dislocation, or implant loosening.
The revision surgery is more complex than the initial hip replacement and requires careful planning and specialized techniques. It involves removing the old prosthesis, addressing any bone loss or damage, and implanting a new one. The goals are to relieve pain, restore function, and improve the patient’s quality of life. Recovery may take longer.
